Maintainers
This part of the documentation is meant for Exegol maintainers. It adds up to the contributors documentation.
Wrapper release
Hint
The wrapper documentation must be aligned with the wrapper features. . The docs PR can be merged once the wrapper is released.
Preparation
1. Git updates
The first step is to update the project and sub-modules, meaning pointing the exegol-images and exegol-resources sub-modules to the latest master version. Even if the wrapper is able to auto-update itself, it is always better to keep the base reference at least up to date.
Update current wrapper repo:
git pull
Update git submodules and checkout to main branch for release:
git -C exegol-docker-build checkout main
git -C exegol-docker-build pull
git -C exegol-resources checkout main
git -C exegol-resources pull
Update to the latest version of the main branches (checkout if needed, except for the wrapper which remains in branch dev)
exegol update -v
Important
Don’t forget to reload and commit any submodule update at this step !
2. Config reviews
Review exegol.utils.ConstantConfig variables
Change version number ! (remove the alpha or beta tag at the end of the version number)
Review documentation
Review README.md
Tests & build
First, test the code with mypy:
mypy exegol.py --ignore-missing-imports --check-untyped-defs
You can execute this one-liner to check the project and build it.
Warning
Require build package installed!
Hint
Exegol can only be published through a source build distribution because of the source code files for building local images.
python3 setup.py clean test && \
(rm -rf Exegol.egg-info && python3 -m build --sdist) || \
echo "Some tests failed, check your code and requirements before publishing!"
Post build
Upgrade tests.test_exegol.py version number to the next version build to avoid future mistake
Commit updates
Publish PR
Wait for review and merge
Manual Upload
Important
PyPi packaging and upload is now handle by GitHub action. It will be triggered with the creation of the new tag in the next-step with the release creation.
This step is no longer needed.
After validation of the PR, we can upload the new version package to pypi.
Warning
Require twine package installed and token configured on ~/.pypirc!
Check package upload on the test repository (optional)
python3 -m twine upload --repository testpypi dist/* --verbose
Upload to the production repository
python3 -m twine upload dist/*
Post-Deploy
Create new github release with new version tag
Fast-forward dev branch to the latest master commit
Change the wrapper version on the dev branch to
x.y.zb1
Images release
Hint
The images documentation must be aligned with the images features. Make sure to add code to the appropriate Exegol docs branch and have a pull request ready. The docs PR can be merged once the images are released.
Prepare changes
The first step consists in preparing the dev branch for merge.
create a pull request
dev -> mainnamedRelease X.Y.Z(Release X.Y.ZbIis also accepted, X, Y, Z and I being numbers. Creating this pull request will trigger the pre-release workflows. The PR comment must indicate all major changes.edit the
devbranch until the pull requests checks (pipeline) all pass, effectively publishing all images to the preproduction Dockerhub registryonce all checks are good, the PR needs to be approved by a maintainer.
Merge changes
Once the PR is approved and ready for merge, it can be merged
merge the PR with Create a merge commit
Synchronize the
devbranch with the latestmainupdate with a fast-forward merge
git checkout main
git pull --all
git checkout dev
git pull --all
git merge --ff-only main
git push
New tag
The X.Y.Z (or X.Y.ZbI) tag then needs to be placed on the same commit the dev and main branches point to.
Optionally, the “Annotated Tag Message” can be set to the PR initial comment with the --file message.txt argument in the git tag command below.
git tag "X.Y.Z"
git push origin --tags
Puhing this tag will trigger the release workflow. Simply put, the workflow will migrate the images from preprod registry to production registry.
Maintainers needs to make sure workflow goes as planned and images end up in the prod Dockerhub registry. If the release fails for some reason, the tag can be deleted, changes pushed, and then the tag can be created again to trigger the release again (git tag -d "X.Y.Z" && git push --delete origin "X.Y.Z").
Publish release
The final step is to create a “release” in github (https://github.com/ThePorgs/Exegol-images/releases/new).
The release must point to the tag created before.
The release must be named
Exegol images X.Y.Z.The release notes can be created with the Generate releases notes button.
Set it as latest release.
Publish
CI/CD Pipeline
The Exegol project relies on a continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipeline for multiple scenarios. At the time of writing, Tue 31 Jan 2023, the pipeline is structured as follows:
The GitHub Actions platform is used on the Exegol module. Its workflows are used for internal and external pull requests, new releases and testing on every commit. The workflows build, and push Python packages on the official PyPI registry, and run tests to make sure everything works as it should.
The GitHub Actions platform is used on the Exegol-images submodule. Its workflows run for internal and external pull requests, new commits, new tags, and allow to:
build AMD64 and ARM64 images on self-hosted runners
run tests to make sure the tools are installed properly
automatically export tools list to the documentation
push the images on the official Dockerhub registry
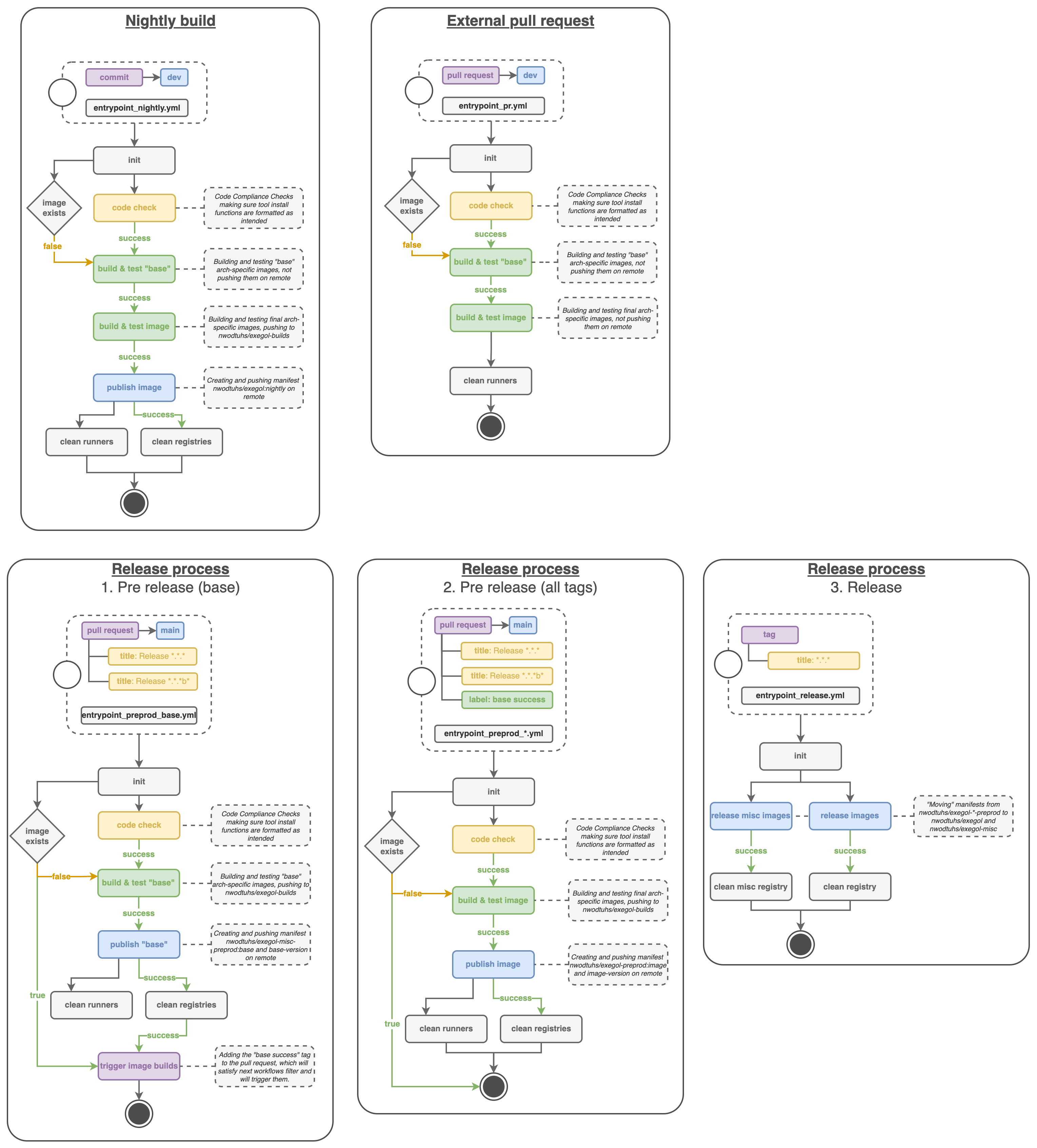
The GitHub Actions platform is used on the Exegol-resources submodule. Its workflows are used to automatically update the resources (monthly) and automatically export the list of resources to the documentation.
The GitHub Actions platform is used for the documentation you’re reading. Its workflows are used to build on every commit and pull request to make sure everything works as it should, but also automatically merge changes between the various branches in order to help with development.
ReadTheDocs then builds the final version on every commit for multiple branches (main, dev, dev-images, dev-wrapper) and hosts it online at https://exegol.readthedocs.io/.
GitHub Actions
The GitHub Actions pipeline(s) need runners to operate the various jobs configured for each workflow. The Exegol project relies on self-hosted runners instead of the GitHub-hosted runners mainly for costing reasons.
At the time of writing, Tue 31 Jan 2023, the Exegol-images pipeline(s) require ARM64 and AMD64 runners in order to build, and run corresponding architectured images.
1. Setting up secrets
There are some operations that the runner will operate that will require authentication, including: - pushing Python packages on PyPI - pushing Docker images on Dockerhub
In order to allow this, GitHub Actions can be set up with secrets that the runner will be able to use later on. This part of the documentation shows what secrets must be set up and how.
API Tokens can be created in the maintainer account’s PyPI account settings, in the API Tokens part. The scope must be set to Project: Exegol. The tokens are linked to the personal PyPI account.
Access Tokens can be created in the maintainer account’s Dockerhub security settings. Permissions must be set to Read, Write, Delete. The tokens are linked to the personal Dockerhub account.
Once the token is created, it can be added as follows:
For Exegol-images, go to the Exegol-images repo settings > secrets > actions. At the time of writing, 11 Feb. 2023, Dockerhub secrets are named
DOCKER_USERNAMEandDOCKER_PASSWORDin the workflows.For the Python wrapper, go to the Exegol repo settings > secrets > actions. At the time of writing, 11 Feb. 2023, the PyPI token is named
PYPI_API_TOKENin the workflows.
2. Deploying a runner
The runner can either run on macOS, Linux, or Windows, as those three operating systems are supporting by the GHA (GitHub Action) platform. x64 and ARM64 are supported for macOS and Windows, and for Linux, ARM is supported as well.
Below are the hardware requirements for each runner:
enough RAM (to be defined)
enough CPU (to be defined)
enough free disk space (at least ~100GB, bare minimum)
Before deploying a GHA agent on a runner, software requirements must be met:
Docker (or Docker Desktop for Windows and macOS)
jq (lightweight and flexible command-line JSON processor)
For Linux systems, Docker is required in order to have the GitHub Actions agent running.
Tip
Docker can be installed quickly and easily with the following command-line:
curl -fsSL "https://get.docker.com/" -o get-docker.sh
sh get-docker.sh
Warning
To run exegol from the user environment without sudo, the user must have privileged rights equivalent to root.
To grant yourself these rights, you can use the following command
# add the sudo group to the user
sudo usermod -aG docker $(id -u -n)
# "reload" the user groups
newgrp
The jq utility is also required and can be installed with the following command line:
apt install jq
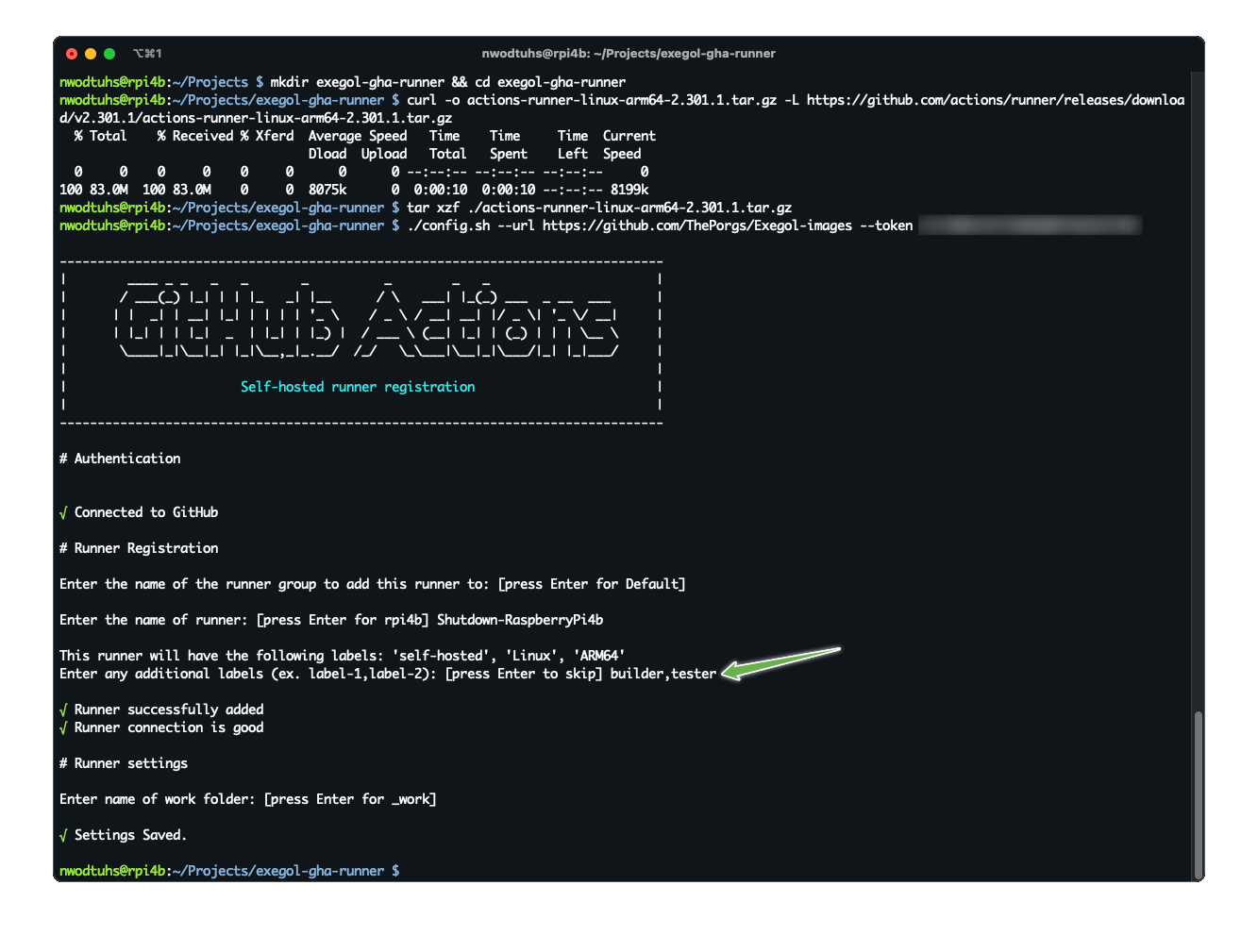
Once the requirements are met, the agent can be deployed as follows (with sufficient permissions in the GitHub repository):
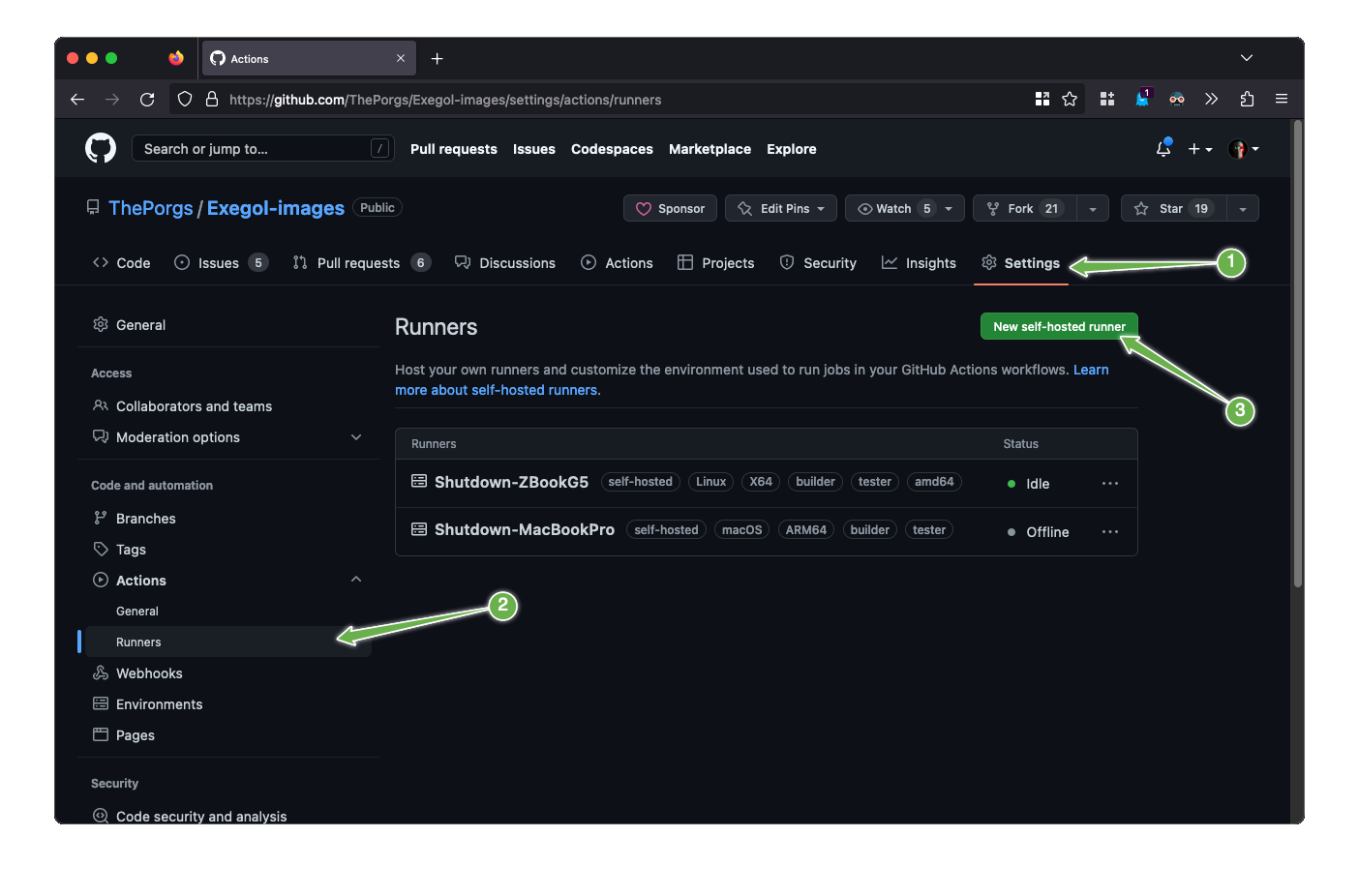
go to https://github.com/ThePorgs/Exegol-images/settings/actions/runners
click on “New self-hosted runner”
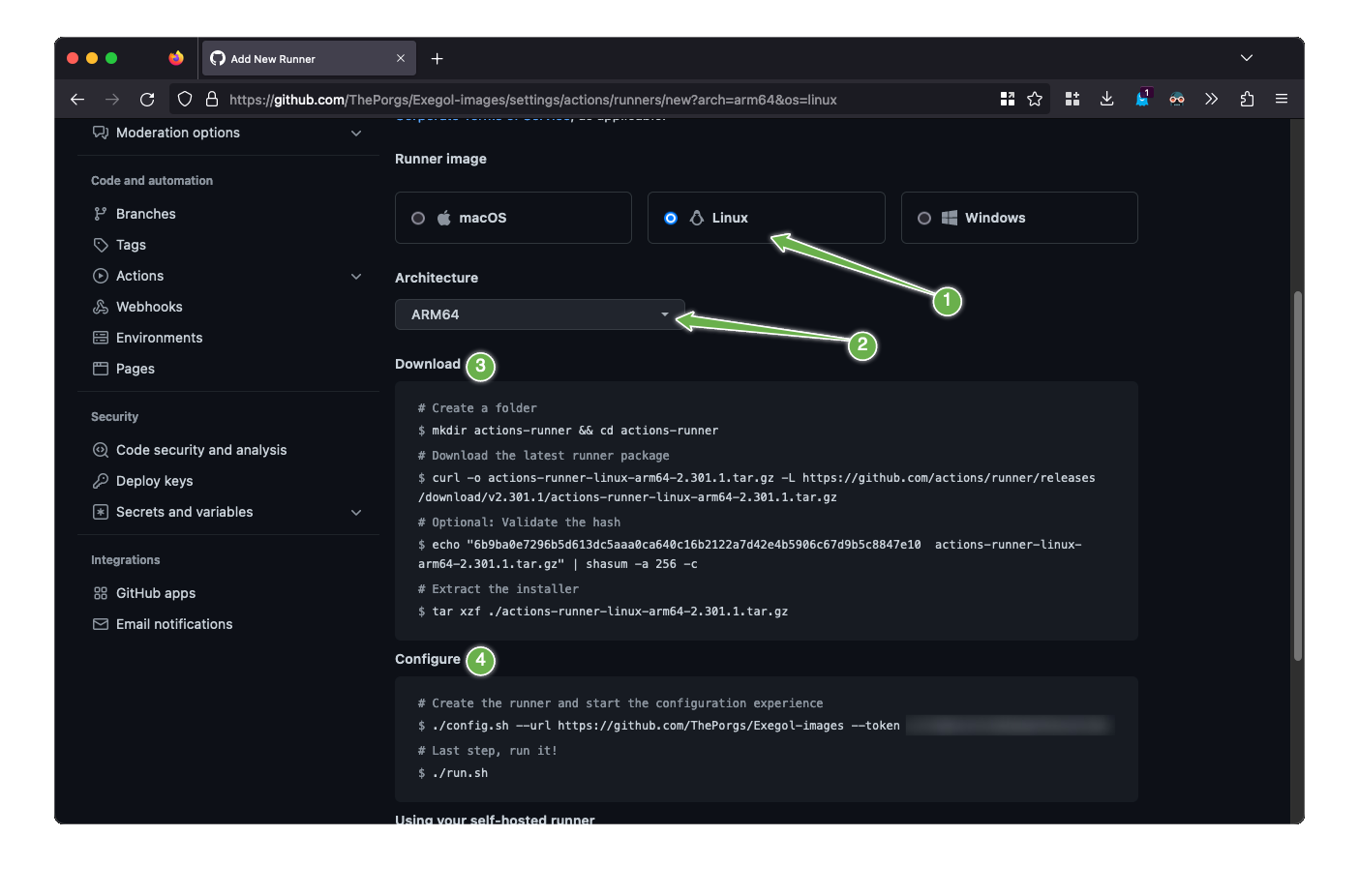
select
Linuxas operating system, as well as the right architecture and follow the instructionswhen running the
config.shscript, the following settings must be setname of the runner group: Default
name of the runner: up to you
additional labels:
builder,tester(adapt this if the runner is to be used for only one of those actions). If the runner is an X64/AMD64, theAMD64tag needs to be set as well. If the runner is ARM64, the right tag will be set automatically.name of work folder: up to you
start the runner with the
run.shscript(option) configure the agent as a service if it is to be run unattended/headless with
sudo ./svc.sh install <user>, more info at https://docs.github.com/en/actions/hosting-your-own-runners/configuring-the-self-hosted-runner-application-as-a-service
Note
When configuring the agent as a service, it will be enabled, meaning it will start at boot. The systemctl is-enabled command should return enabled.
sudo systemctl is-enabled actions.runner.ThePorgs-Exegol-images.<runner-name>.service
In order to start the service, either reboot the runner, or use systemctl.
sudo systemctl start actions.runner.ThePorgs-Exegol-images.<runner-name>.service
Note
Screenshots annotated with https://annotely.com/
For macOS, Docker Desktop must be installed: https://docs.docker.com/desktop/install/mac-install/.
In
Settings > Resources > Advanced, thevirtual disk limitmust be set to at least 100GB.In
Settings > Resources > Advanced, allocate enough CPUs, Memory and Swap.
The jq tool can be installed as follows.
# install brew
ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)" < /dev/null 2> /dev/null
# install jq
brew install jq
Xcode Command Line Tools are also required, and they can be installed with the following command line.
xcode-select --install
Once the requirements are met, the agent can be deployed as follows (with sufficient permissions in the GitHub repository):
go to https://github.com/ThePorgs/Exegol-images/settings/actions/runners
click on “New self-hosted runner”
select
macOSas operating system, as well as the right architecture and follow the instructionswhen running the
config.shscript, the following settings must be setname of the runner group: Default
name of the runner: up to you
additional labels:
builder,tester(adapt this if the runner is to be used for only one of those actions). If the runner is an X64/AMD64, theAMD64tag needs to be set as well. If the runner is ARM64, the right tag will be set automatically.name of work folder: up to you
start the runner with the
run.shscriptthe agent must not be configured as a service with
./svc.sh install. Some errors have been raised when setting up the pipeline like this.
Note
TODO : how to make that service run at boot unattended without using svc.sh install?
3. Checking runners status
Go to https://github.com/ThePorgs/Exegol-images/settings/actions/runners
4. Understanding the pipelines
TODO explain the pipelines, include diagrams.
4. Common errors
1. docker login
When configuring a macOS agent as a service with ./svc.sh install, the following error was met during workflow run.
Run docker/login-action@v2
with:
username: ***
password: ***
ecr: auto
logout: true
Logging into Docker Hub...
Error: Error saving credentials: error storing credentials - err: exit status 1, out: `error storing credentials - err: exit status 1, out: `User interaction is not allowed.``
In order to avoid that error, the runner was started interactively with ./run.sh.
2. Disk space
When there’s not enough disk space, the following error is usually raised by the pipelines.
You are running out of disk space. The runner will stop working when the machine runs out of disk space. Free space left: 62 MB
Pull Requests
When handling pull requests, maintainers may need to synchronize a contributor’s fork with latests changes. In command-line, this can be achieved as follows.
git clone "git@github.com:USER/FORK" "dest_dir"
cd dest_dir
git remote add upstream "git@github.com:ThePorgs/REPO"
git fetch upstream
git checkout "TARGET_FORK_BRANCH"
git merge --no-edit upstream/"ORIGIN_BRANCH"
# solve conflicts if any
git push